We love hearing about and reading new research involving AFM and SPM here at NuNano, whether or not our probes are involved. AFM continues to push into new scientific territories, bringing back remarkable data and images from the nanoscale.
Our annual top-paper list is shaped both by recommendations from the AFM community and by suggestions from the NuNano team. This year’s long list was longer than ever, but we’ve trimmed it down to twelve, one for each month of the year! We aimed for diversity: different research groups, different countries, and a broad set of applications.
These papers highlight the expanding reach of AFM. Some studies develop flexible, eco-friendly conductive materials or advance AFM techniques for probing energy devices and interfacial forces. Others use AFM to reveal how supramolecular networks nucleate and grow, how 2D materials form moiré superlattices, and how ferroelectric domain walls move over surprisingly long distances.
In the biological realm, AFM has been employed to uncover how immune cells enter lymphatic vessels, how septin proteins organize on membranes, and how bacteria build biofilms and release extracellular vesicles. It also demonstrates how subtle nanomechanical differences in therapeutic antibodies can affect their performance in cancer treatment.
Here is our list in alphabetical order:
1. Cristiano Albonetti, Carlo Gotti, Luca Pasquini, Nicola Gilli, Fabiola Liscio, Angela Longo, Stefano Chiodini, Franco Dinelli, Maria Letizia Focarete, Mirko Seri, Monica Bertoldo & Piera Maccagnani; Electro-Mechanical Properties of Metallized Sodium Alginate Foils at the Limit of the Electrical Conduction (2025) ACS Omega 10 (29)
Gold-coated sodium alginate substrates combine flexibility and conductivity, showing reproducible resistance changes under stress, making them promising eco-friendly strain sensors.
2. Hüsnü Aslan, Khaled Kaja, José Morán-Meza, François Piquemal, José Alvarez, Nicolas Chauvin, José Penuelas, Steffan Møller Sønderskova and Philippe Regrenye; Atomic force microscopy as a multimetrological platform for energy devices (2025) Nanoscale 14
AFM enables detailed nanoscale characterization of nanowires, revealing their structural, electrical, and spectroscopic properties. Through this work, AFM establishes itself as an essential metrological tool for the development of advanced energy-harvesting devices.
3. Fouzia Bano, Suneale Banerji, Tao Ni, Dixy E. Green, Kalila R. Cook, Iain W. Manfield, Paul L. DeAngelis, Emanuele Paci, Martin Lepšík, Robert J. C. Gilbert, Ralf P. Richter & David G. Jackson Structure and unusual binding mechanism of the hyaluronan receptor LYVE-1 mediating leucocyte entry to lymphatics (2025) Nature Communications 16: 2754
This work studies LYVE-1 interaction mechanism using AFM dynamic force spectroscopy, showing that LYVE-1 enables immune cells lymphatic entry via a unique “sliding” interaction with hyaluronic acid. This peculiar interaction allows cells to move through endothelial junctions efficiently while maintaining adhesion for downstream functions.
4. Simone Bengalia & Stefano Chiodini; Quantification of solvation forces with amplitude modulation AFM (2025) Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 685, 342-349
A new matrix-based AFM force-reconstruction method recovers the full tip–sample interaction at solid–liquid interfaces, including previously inaccessible monotonic forces, enabling quantitative studies of interfacial properties and their effects on colloid science.
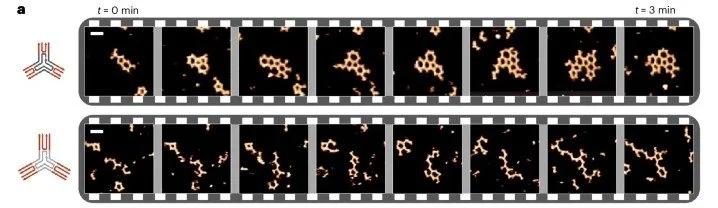
5. Vincenzo Caroprese, Cem Tekin, Veronika Cencen, Majid Mosayebi, Navid Asmari, Tanniemola B. Liverpool, Derek N. Woolfson, Georg E. Fantner & Maartje M. C. Bastings; Interface flexibility controls the nucleation and growth of supramolecular networks (2025) Nature Chemistry 17, 325–333
The study shows that “interface flexibility” in macromonomers critically controls supramolecular network nucleation and growth, with excess flexibility disrupting assembly; tuning this parameter expands design options for synthetic materials.
Time-lapse of short (top) and long (bottom) 3PS self-assembly over 3 min, highlighting the difference in nucleation. Snapshots are taken from full-length time series. Taken from https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-01741-y
6. James A. Goodchild, Brandy N. Curtis, Yangang Pan, Yining Jiang, Fang Jiao, Amy S. Gladfelter & Simon Scheuring; Septin higher-order structure on yeast membranes in vitro (2025) Nature Communications 16, 5055
HS-AFM reveals that yeast septins assemble on liquid-disordered membrane phases, forming aligned single filaments that self-template and stack into organized 3D structures, showing that septins intrinsically encode their mesoscale organization.
7. Camila Leiva-Sabadini, Pablo Berríos, Paula Saavedra, Javiera Carrasco-Rojas, José Vicente González-Aramundiz, Mario Vera, Estefanía Tarifeño-Saldivia, Christina M. A. P. Schuh & Sebastian Aguayo; Biofilm formation on collagen substrates modulates Streptococcus mutans bacterial extracellular nanovesicle production and cargo (2025) Nanoscale Adv. 7, 5670-5680
AFM shows that S. mutans biofilm formation on native and glycated collagen produces smaller, less abundant extracellular vesicles with altered morphology, enriched in virulence and metabolic proteins, impacting oral disease development.
Methylglyoxal (MGO) glycation of type-I collagen-coated surfaces allows S. mutans biofilm formation. Taken from https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2025/na/d5na00248f
8. Ruben Millan-Solsona, Spenser R. Brown, Lance Zhang, Sita Sirisha Madugula, HuanHuan Zhao, Blythe Dumerer, Amber N. Bible, Nickolay V. Lavrik, Rama K. Vasudevan, Arpan Biswas, Jennifer L. Morrell-Falvey, Scott Retterer, Martí Checa & Liam Collins; Analysis of biofilm assembly by large area automated AFM (2025) npj Biofilms and Microbiomes 11, 75
An automated large-area AFM method, enhanced with machine learning, captures millimetre-scale, high-resolution biofilm structure. It reveals early spatial organisation, preferred cell orientation, and flagella-driven interactions, offering a powerful tool for studying and controlling bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation.
9. Hannah Seferovic, Patricia Sticht, Lisa Hain, Rong Zhu, Sebastian Diethör, Christian Wechselberger, Florian Weber, David Bernhard, Birgit Plochberger, Yoo Jin Oh, Javier Chaparro-Riggers & Peter Hinterdorfer; Nanomechanical binding mechanism of ligands drives agonistic activity (2025) Nature Communications 16, 6674
The study elucidates how therapeutic anti-CD40 antibodies used in cancer treatment compare to the natural CD40 Ligand. Thanks to this comparison, the distinct binding mechanism of natural ligand is uncovered, providing useful insights for the optimisation of future anti-CD40 antibodies and the development of new antibody- based cancer treatments.
10. William Trewby, Mahdi Tavakol & Kislon Voïtchovsky; Local mapping of the nanoscale viscoelastic properties of fluid membranes by AFM nanorheology (2025) Nature Communications 16, 3842
A new AFM method maps nanoscale lipid mobility in unlabelled membranes, revealing that diffusion is highly localised in biomembranes varying sharply over tens of nanometers.
Nanoscale diffusivity mapping of a native bovine eye lens membrane. Taken from https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-59260-w
11. Manuel Zahn, Aaron Merlin Müller, Kyle P. Kelley, Sabine Neumayer, Sergei V. Kalinin, István Kézsmarki, Manfred Fiebig, Thomas Lottermoser, Neus Domingo, Dennis Meier & Jan Schultheiß; Reversible long-range domain wall motion in an improper ferroelectric (2025) Nature Communications; 16: 1781
The work shows that improper ferroelectric ErMnO₃ exhibits naturally reversible domain wall motion over unusually long distances (>250 nm), enabled by its intrinsic topology. These results offer new insights in improper ferroelectrics and ensure device stability for various applications such as tuneable capacitors or sensors.
12. Gaolei Zhan, Brecht Koek, Yijia Yuan, Yikuan Liu, Vipin Mishra, Veniero Lenzi, Karol Strutyński, Chunxiao Li, Rongrong Zhang, Xin Zhou, Hwa Seob Choi, Zhen-Feng Cai, Joaquín Almarza, Kunal S. Mali, Aurelio Mateo-Alonso, Manuel Melle Franco, Yihan Zhu, Steven De Feyter & Kian Ping Loh; Moiré two-dimensional covalent organic framework superlattices (2025) Nature Chemistry 17, 518–524
The work presents a method to synthesize 2D polymer bilayers with controllable stacking, showing how monomers and solvents tune stacking modes and can generate large-area moiré superlattices with customizable properties.
What did you think? What have we missed off the list? Please do feel free to send us your thoughts and any favourite papers that you would recommend we add to our January reading list by emailing us community@nunano.com
If you enjoyed this blog post you may also like our Top Papers of 2024 or Top Papers of 2023